Notes to accompany 2nd Year Undergraduate City University Clinical Practice Lecture
Dr Simon Barnard
PhD BSc FCOptom FAAO DCLP
Accommodation
The facility enabling the change in dioptric power of the crystalline lens thereby altering the focus of the eye
Assessment of accommodation

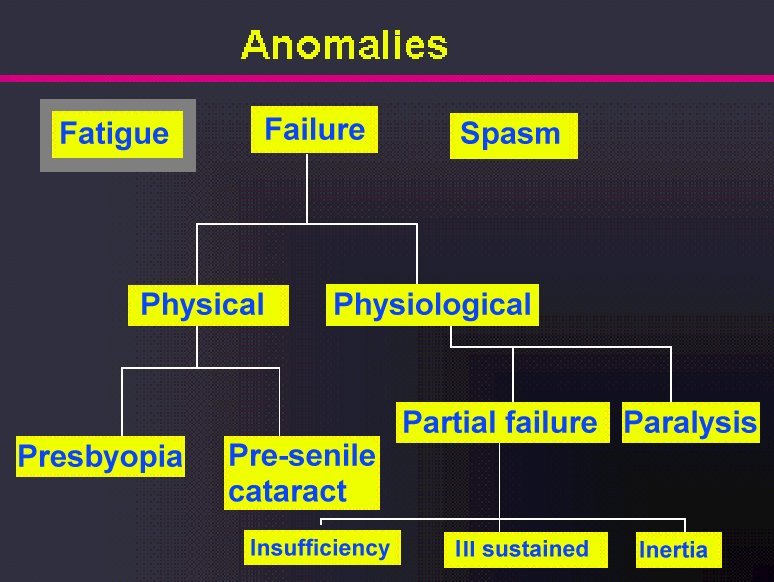
Accommodative fatigue
Apart from overuse, factors that influence onset of fatigue include
Symptoms of accommodative fatigue
Treatment of fatigue
Failure of accommodation
Presbyopia
Age of onset
Symptoms of presbyopia
Patients complain of reading difficulty in poor light, tired eyes after reading and BLURRED VISION for reading
Management
Prescribe correction so that near point of focus is brought within normal working distance
Determination of reading addition
(b) measure amplitudes of accommodation
(c) use amplitudes as a STARTING point to calculate an approximate reading addition
Rule of thumb - leave 1/3rd accommodation in reserve
Check clarity and range. Double check with +&- additions
Pre-senile cataract
Cataract is likely to reduce accommodation
May be unilateral
Unequal reading adds ?
May have reduced VA
Insufficiency of accommodation
Aetiology of insufficiency
Symptoms of insufficiency
Investigation of insufficiency
Exclude...
Local cause
Central cause
General cause
Treatment management of insufficiency
Ill sustained accommodation
Amplitudes are normal but rapidly diminish with use. Is this the start of a true insufficiency ?…or… rapid onset fatigue ?
Aetiology of Ill sustained accommodation
Investigation & Treatment
Inertia of accommodation
Difficulty in changing focus from distance to near and vice versa
Diagnosis often based on symptomatology
Aetiology/associations
Treatment
Paralysis of accommodation
May be partial or total, unilateral or bilateral
Signs and symptoms
More accommodative effort required to see near object which is then perceived to be nearer than it actually is and therefore smaller
What does N IIIrd innervate ? ………………….
Aetiology
Management
Spasm of accommodation
Tone of ciliary muscle is increased and a constant accommodative effort is expended by the parasympathetic nervous system. Pseudomyopia produced
Symptoms
Investigation
Aetiology
Spasm can be further categorised into:
(a) Functional spasm
(b) Organic spasm
Functional spasm
A response to over fatigue and "eye strain". Precipitated by 3 factors:
Treatment of functional spasm
Organic spasm
Irritation of parasympathetic system
Aetiology
- drug induced e.g., physostigmine, pilocarpine, morphine, digitalis
- lesions of brain stem and OM trunk
e.g., anterior uveitis
e.g., diphtheria, tooth extraction
Treatment of organic spasm
Summary
Acknowledgements & further reading
Heinemann, Oxford
Simon Barnard November 1999
To see Accommodation in Action, click here.